The lumbar spine contains a total of 5 intervertebral discs situated between the vertebral bodies. The primary functions of these discs are to1: Distribute compressive loads placed on the spine, providing shock absorption properties. Maintain the distance between the vertebral bodies during movement. Lumbar disc disease is the drying out of the spongy interior matrix of an intervertebral disc in the spine. Many physicians and patients use the term lumbar disc disease to encompass several different causes of back pain or sciatica. It is thought that lumbar disc disease causes about one-third of all back pain.
Lumbar disc Symptoms :
Pain, loss of muscle strength and loss of touch sensation may occur if this herniation causes the compression of the most proximal part of the nerve closely neighbouring the intervertebral disc material. Pain is in the distribution of the nerve compressed, usually down the back of the leg, side of the calf and inside of the foot (sciatica).
What are the symptoms of lumbar disk disease?
Intermittent or continuous back pain
Spasm of the back muscles
Sciatica
Muscle weakness in the legs
Numbness in the leg or foot
Decreased reflexes at the knee or ankle
Changes in bladder or bowel function
Lumbar disc Treatment :
Initial treatment in lumbar disc disease is one or two days of bedrest (although growing number of studies shows that it makes little difference) and pain relieving medications. In cases with ongoing pain despite conservative treatments, a surgical operation that will remove the compressing disc material, a microdiscectomy or discectomy may be recommended to treat a lumbar disc herniation.
Physical therapy, exercise and gentle stretching to help relieve pressure on the nerve root
Ice and heat therapy for pain relief
Manipulation (such as chiropractic manipulation)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen or COX-2 inhibitors for pain relief
Narcotic pain medications for pain relief
Oral steroids to decrease inflammation for pain relief
Epidural injections to decrease inflammation for pain relief
herniated disc
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.
herniated disc Signs and symptoms:
Typically, symptoms are experienced on one side of the body only.Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the types of soft tissue involved. They can range from little or no pain, if the disc is the only tissue injured, to severe and unrelenting neck pain or low back pain that radiates into regions served by nerve roots which have been irritated or impinged by the herniated material. Often, herniated discs are not diagnosed immediately, as patients present with undefined pains in the thighs, knees, or feet.
herniated disc Treatment :
In the majority of cases spinal disc herniation can be treated successfully conservatively, without surgical removal of the herniated material. Sciatica is a set of symptoms associated with disc herniation. A study on sciatica showed that about one-third of patients with sciatica recover within two weeks after presentation using conservative measures alone, and about three-quarters of patients recovered after three months of conservative treatment. However the study did not indicate the number of individuals with sciatica that had disc herniations.
herniated disc Surgery:
Surgery may be useful when a herniated disc is causing significant pain radiating into the leg, significant leg weakness, bladder problems, or loss of bowel control.
Discectomy (the partial removal of a disc that is causing leg pain) can provide pain relief sooner than non-surgical treatments.
Small endoscopic discectomy (called nano-endoscopic discectomy) is non-invasive and does not cause failed back syndrome.
Invasive microdiscectomy with a one-inch skin opening has not been shown to result in a significantly different outcome from larger-opening discectomy with respect to pain.It might however have less risk of infection.
Failed back syndrome is a significant, potentially disabling, result that can arise following invasive spine surgery to treat disc herniation. Smaller spine procedures such as endoscopic transforaminal lumbar discectomy cannot cause failed back syndrome, because no bone is removed.
The presence of cauda equina syndrome (in which there is incontinence, weakness, and genital numbness) is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention and possibly surgical decompression.
causes of lumbar disc herniation :
Lumbar herniated disc most often affects people aged 35 to 50. Disc herniation symptoms usually start for no apparent reason. Or they may occur when a person lifts something heavy and/or twists the lower back, motions that put added stress on the discs.A single excessive strain or injury may cause a herniated disc. However, disc material degenerates naturally as one ages, and the ligaments that hold it in place begin to weaken. As this degeneration progresses, a relatively minor strain or twisting movement can cause a disc to rupture.
Disc herniation can occur in any disc in the spine, but the two most common forms are lumbar disc herniation and cervical disc herniation. The former is the most common, causing low back pain (lumbago) and often leg pain as well, in which case it is commonly referred to as sciatica.
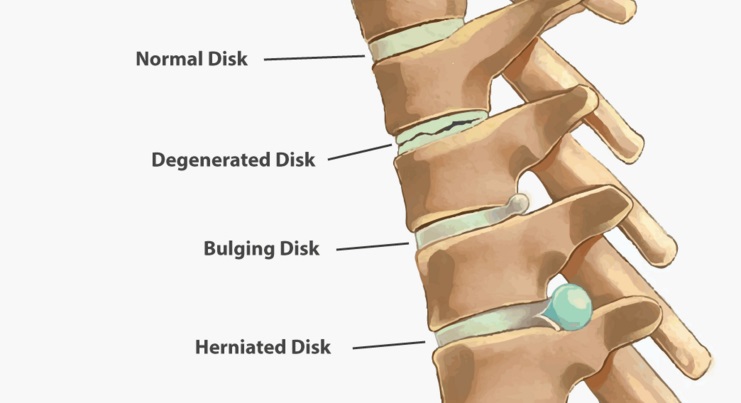
waist disk Frequently Asked Questions ؟
What is the cause of lumbar disc disease?
Lumbar disk disease is caused by a change in the structure of the normal disk. Most of the time, disk disease happens as a result of aging and the normal break down that occurs within the disk. Sometimes, severe injury can cause a normal disk to herniate. Injury may also cause an already herniated disk to worsen.
How serious is a compressed disc?
Permanent nerve damage.Without treatment, compressed nerve roots in the spine can be permanently damaged, leading to chronic pain, weakness, and loss of sensation. Other rare but serious complications of a protruding disc include cauda equina syndrome, saddle anesthesia, and bowel and bladder dysfunction.
What happens if a bulging disc goes untreated?
A severe case of a bulging disc can cut off nerve impulses, even causing permanent nerve damage. Additionally, you may experience sharp paints, incontinence, bowel movement irregularity, or even partial paralysis as the issue worsens.
What will a doctor do for a bulging disc?
Injections. If rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy don’t help with your pain, your doctor can inject a steroid medicine into the space around your spinal nerve. This is called an epidural injection. The steroid can help bring down the swelling, help you move more easily, and ease pain from a herniated disk.
Can a collapsed disc heal itself?
The good news is that in most cases — 90% of the time — pain caused by a herniated disc will go away on its own within six months. Initially, your doctor will likely recommend that you take an over-the-counter pain reliever and limit activities that cause pain or discomfort.
Is walking good for bulging disc?
Absolutely. Walking is an excellent choice for patients with herniated discs, as it stimulates blood flow and oxygen to the cells. It also helps keep your discs hydrated, which is important for healing. Other low-impact aerobic activities to try are swimming and cycling.
Can you push a bulging disc back in?
If you have back pain from a bulging disc, do not have your friend try to force it back into place. This will likely increase, rather than relieve, your pain.
How long does a ruptured disk take to heal?
The average amount of time it takes for a herniated disk to heal is four to six weeks, but it can get better within a few days depending on how severe the herniation was and where it occurred. The biggest factor in healing a herniated disk is time, because most often it will resolve on its own.