by best-mag | medicine
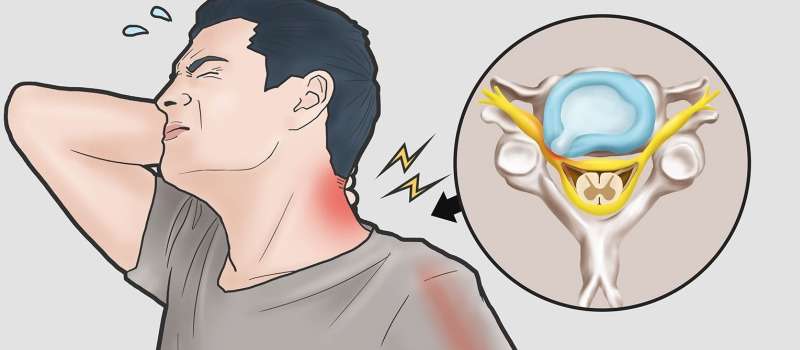
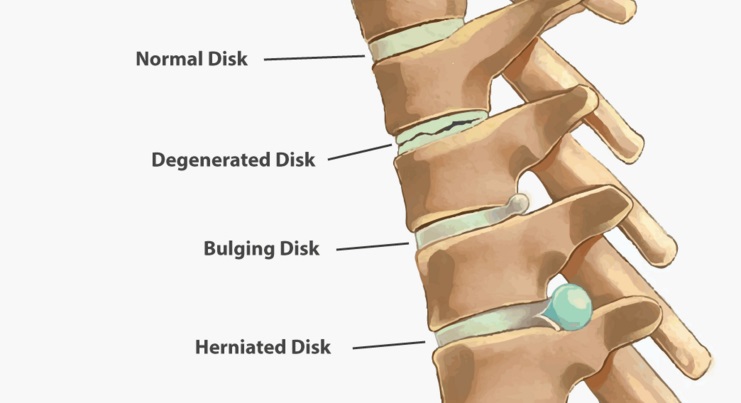
A cervical disc is a shock-absorbing, soft pad that lies between vertebrae in the cervical spine (the neck). The cervical spine is comprised of six total cervical discs. With the natural wear and tear that accompanies aging, a cervical disc may begin to degenerate, with some patients not even experiencing any symptoms.Cervical discs support the neck’s vertebral bones while also enabling flexibility for head movements. Sitting between adjacent cervical vertebrae stacked atop each other, each cervical disc acts as a shock absorber to help the cervical spine handle various stresses and loads.Cervical degenerative disc disease is a common cause of neck pain and radiating arm pain. It develops when one or more of the cushioning discs in the cervical spine starts to break down due to wear and tear.A bulging disc in your neck may be relatively painless. Or it can cause severe pain in your neck, as well as your shoulders, chest, and arms. It may also cause numbness or weakness in your arms or fingers. Sometimes, this pain and numbness may even cause you to think that you’re having a heart attack.
What is cervical disc ?
The
cervical disks are
the cushions that lie between the cervical vertebrae. They act as shock absorbers to allow your neck to move freely. Your cervical spine also forms a protective tunnel for the upper part of your spinal cord to pass through.Symptoms of c5-c6 disc herniation can include numbness, tingling, burning, weakness, problems with vision, and more.
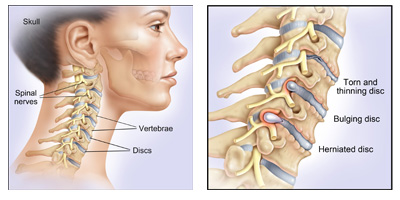
What is a cervical herniated disc ?
Cervical discs are the cushions between the vertebrae in the upper back and neck. Herniation of the disc occurs when the gelatinous inner disc material, the nucleus pulpous, ruptures, or herniates, through the outer cervical disc wall.Cervical disc herniation is the result of the displacement of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc, which may result in impingement of these traversing nerves as they exit the neural foramen or directly compressing the spinal cord contained within the spinal canal.In some patients, a cervical herniated disc can cause spinal cord compression, where disc material pushes on the spinal cord. This is a much more serious condition and may require a more aggressive treatment plan. Spinal cord compression symptoms include: Awkward or stumbling gait.
Most cases of cervical herniated disc pain can be successfully managed with nonsurgical treatments, such as over-the-counter pain medications, physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the neck, ice or heat packs, and/or activity modifications to avoid painful movements until the pain has subsided.Treatment with rest, pain medication, spinal injections, and physical therapy is the first step to recovery. Most people improve in 6 weeks and return to normal activity. If symptoms continue, surgery may be recommended.In most cases cervical disc herniations improve with time and symptomatic treatment. This can take 6-12 weeks. Improvement is usually seen within 2-3 weeks and full recovery in the ensuing 2-3 months.
cervical disc surgery :
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a surgery to remove a herniated or degenerative disc in the neck. An incision is made in the throat area to reach and remove the disc. A graft is inserted to fuse together the bones above and below the disc.Cervical disk replacement surgery involves removing a diseased cervical disk and replacing it with an artificial disk. Before this procedure was available, the affected disk was removed and the vertebrae above and below were fused together to prevent motion.The success rate of cervical spine surgery is very high, but complications have been reported. “The take away is that most of the complications were very rare, some were almost nonexistent,” Buser and Wang said. “Dural tear and C5 palsy were the most common, but again, they had a very low frequency.
spine MRI :
A cervical (SER-vih-kul) spine MRI can detect a variety of conditions in the neck and upper back area, including problems with the soft tissues within the spinal column, such as the spinal cord, nerves, and disks.MRI can produce the most reliable snapshot of the spine that promotes the accurate diagnosis of a herniated disc.A cervical MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan uses energy from strong magnets to create pictures of the part of the spine that runs through the neck area (cervical spine). MRI does not use radiation (x-rays). Single MRI images are called slices. The images can be stored on a computer or printed on film.
Questions About Cervical Disk Disease ?
Is walking good for herniated disc?
Absolutely. Walking is an excellent choice for patients with herniated discs, as it stimulates blood flow and oxygen to the cells. It also helps keep your discs hydrated, which is important for healing. Other low-impact aerobic activities to try are swimming and cycling
Is bed rest good for slipped disc?
The optimal sleeping position for a herniated disc is on your back. Lying on your back keeps your spine in a neutral position so you have less chance of pinching the nerve. For added comfort, nestle a small pillow or rolled-up towel under your knees and lower back.Most often 1-2 days of strict bed rest will calm severe back pain. Bed rest should not exceed 48 hours. Once you are back into your daily routine, you should take frequent rest breaks throughout the day- but avoid sitting for long periods of time.If you have a herniated disc, you may want to try sleeping on your side curled in a fetal position:
-Lay on your back and then roll over gently onto your side.
-Tuck your knees toward your chest and gently curl your torso toward your knees.
-Remember to switch sides from time to time to prevent any imbalances.
Is a hot bath good for a slipped disc?
Applying Heat, via a heating pad or heat wrap, even a hot bath may help muscle spasms in the first 2 days of initial pain. Heat helps soft issues to stretch, dilates blood vessels and decreases pain signals giving some relief to the discomfort.
Does massage help slipped disc?
Deep Tissue Massage: There are more than 100 types of massage, but deep tissue massage is an ideal option if you have a herniated disc because it uses a great deal of pressure to relieve deep muscle tension and spasms, which develop to prevent muscle motion at the affected area.
What happens if a cervical herniated disc goes untreated?
Untreated herniated discs with symptoms can become more painful and debilitating as time goes on. You may also experience bladder and bowel dysfunction and saddle anesthesia, so-called because it affects the areas on your body that would touch a saddle if you were sitting on a horse.
Is cervical surgery safe?
Although cervical disc surgery is generally safe, it does have a few risks, including.Some risks related to neck surgery can include:
bleeding or hematoma at the surgical site.
infection of the surgical site.
injury to the nerves or spinal cord.
leakage of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
C5 palsy, which causes paralysis in the arms.
degeneration of areas adjacent to the surgical site.
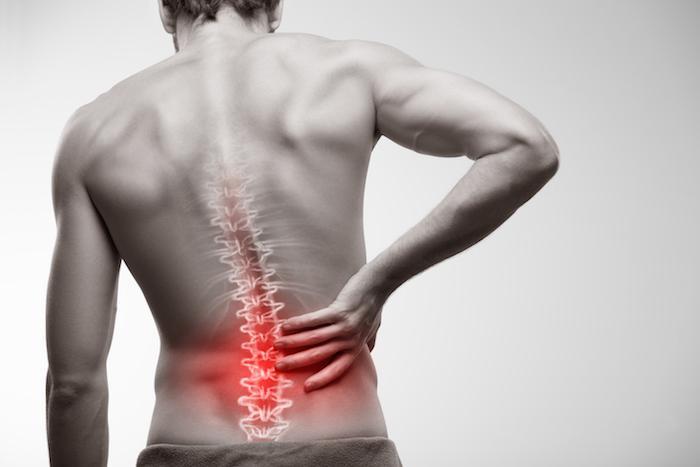
by best-mag | medicine
The lumbar spine contains a total of 5 intervertebral discs situated between the vertebral bodies. The primary functions of these discs are to1: Distribute compressive loads placed on the spine, providing shock absorption properties. Maintain the distance between the vertebral bodies during movement. Lumbar disc disease is the drying out of the spongy interior matrix of an intervertebral disc in the spine. Many physicians and patients use the term lumbar disc disease to encompass several different causes of back pain or sciatica. It is thought that lumbar disc disease causes about one-third of all back pain.
Lumbar disc Symptoms :
Pain, loss of muscle strength and loss of touch sensation may occur if this herniation causes the compression of the most proximal part of the nerve closely neighbouring the intervertebral disc material. Pain is in the distribution of the nerve compressed, usually down the back of the leg, side of the calf and inside of the foot (sciatica).
What are the symptoms of lumbar disk disease?
Intermittent or continuous back pain
Spasm of the back muscles
Sciatica
Muscle weakness in the legs
Numbness in the leg or foot
Decreased reflexes at the knee or ankle
Changes in bladder or bowel function
Lumbar disc Treatment :
Initial treatment in lumbar disc disease is one or two days of bedrest (although growing number of studies shows that it makes little difference) and pain relieving medications. In cases with ongoing pain despite conservative treatments, a surgical operation that will remove the compressing disc material, a microdiscectomy or discectomy may be recommended to treat a lumbar disc herniation.
Physical therapy, exercise and gentle stretching to help relieve pressure on the nerve root
Ice and heat therapy for pain relief
Manipulation (such as chiropractic manipulation)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen or COX-2 inhibitors for pain relief
Narcotic pain medications for pain relief
Oral steroids to decrease inflammation for pain relief
Epidural injections to decrease inflammation for pain relief
herniated disc
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.
herniated disc Signs and symptoms:
Typically, symptoms are experienced on one side of the body only.Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the types of soft tissue involved. They can range from little or no pain, if the disc is the only tissue injured, to severe and unrelenting neck pain or low back pain that radiates into regions served by nerve roots which have been irritated or impinged by the herniated material. Often, herniated discs are not diagnosed immediately, as patients present with undefined pains in the thighs, knees, or feet.
herniated disc Treatment :
In the majority of cases spinal disc herniation can be treated successfully conservatively, without surgical removal of the herniated material. Sciatica is a set of symptoms associated with disc herniation. A study on sciatica showed that about one-third of patients with sciatica recover within two weeks after presentation using conservative measures alone, and about three-quarters of patients recovered after three months of conservative treatment. However the study did not indicate the number of individuals with sciatica that had disc herniations.
herniated disc Surgery:
Surgery may be useful when a herniated disc is causing significant pain radiating into the leg, significant leg weakness, bladder problems, or loss of bowel control.
Discectomy (the partial removal of a disc that is causing leg pain) can provide pain relief sooner than non-surgical treatments.
Small endoscopic discectomy (called nano-endoscopic discectomy) is non-invasive and does not cause failed back syndrome.
Invasive microdiscectomy with a one-inch skin opening has not been shown to result in a significantly different outcome from larger-opening discectomy with respect to pain.It might however have less risk of infection.
Failed back syndrome is a significant, potentially disabling, result that can arise following invasive spine surgery to treat disc herniation. Smaller spine procedures such as endoscopic transforaminal lumbar discectomy cannot cause failed back syndrome, because no bone is removed.
The presence of cauda equina syndrome (in which there is incontinence, weakness, and genital numbness) is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention and possibly surgical decompression.
causes of lumbar disc herniation :
Lumbar herniated disc most often affects people aged 35 to 50. Disc herniation symptoms usually start for no apparent reason. Or they may occur when a person lifts something heavy and/or twists the lower back, motions that put added stress on the discs.A single excessive strain or injury may cause a herniated disc. However, disc material degenerates naturally as one ages, and the ligaments that hold it in place begin to weaken. As this degeneration progresses, a relatively minor strain or twisting movement can cause a disc to rupture.
Disc herniation can occur in any disc in the spine, but the two most common forms are lumbar disc herniation and cervical disc herniation. The former is the most common, causing low back pain (lumbago) and often leg pain as well, in which case it is commonly referred to as sciatica.
waist disk Frequently Asked Questions ؟
What is the cause of lumbar disc disease?
Lumbar disk disease is caused by a change in the structure of the normal disk. Most of the time, disk disease happens as a result of aging and the normal break down that occurs within the disk. Sometimes, severe injury can cause a normal disk to herniate. Injury may also cause an already herniated disk to worsen.
How serious is a compressed disc?
Permanent nerve damage.Without treatment, compressed nerve roots in the spine can be permanently damaged, leading to chronic pain, weakness, and loss of sensation. Other rare but serious complications of a protruding disc include cauda equina syndrome, saddle anesthesia, and bowel and bladder dysfunction.
What happens if a bulging disc goes untreated?
A severe case of a bulging disc can cut off nerve impulses, even causing permanent nerve damage. Additionally, you may experience sharp paints, incontinence, bowel movement irregularity, or even partial paralysis as the issue worsens.
What will a doctor do for a bulging disc?
Injections. If rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy don’t help with your pain, your doctor can inject a steroid medicine into the space around your spinal nerve. This is called an epidural injection. The steroid can help bring down the swelling, help you move more easily, and ease pain from a herniated disk.
Can a collapsed disc heal itself?
The good news is that in most cases — 90% of the time — pain caused by a herniated disc will go away on its own within six months. Initially, your doctor will likely recommend that you take an over-the-counter pain reliever and limit activities that cause pain or discomfort.
Is walking good for bulging disc?
Absolutely. Walking is an excellent choice for patients with herniated discs, as it stimulates blood flow and oxygen to the cells. It also helps keep your discs hydrated, which is important for healing. Other low-impact aerobic activities to try are swimming and cycling.
Can you push a bulging disc back in?
If you have back pain from a bulging disc, do not have your friend try to force it back into place. This will likely increase, rather than relieve, your pain.
How long does a ruptured disk take to heal?
The average amount of time it takes for a herniated disk to heal is four to six weeks, but it can get better within a few days depending on how severe the herniation was and where it occurred. The biggest factor in healing a herniated disk is time, because most often it will resolve on its own.
by best-mag | medicine
The brains of humans and other vertebrates are composed of very soft tissue and have a gelatin-like texture. Living brain tissue has a pink tint in color on the outside (gray matter), and nearly complete white on the inside (white matter), with subtle variations in color. The three largest divisions of the brain are:
Cerebral cortex
Brainstem
Cerebellum
These areas are composed of two broad classes of cells: neurons and glia. These two types are equally numerous in the brain as a whole, although glial cells outnumber neurons roughly 4 to 1 in the cerebral cortex. Glia come in several types, which perform a number of critical functions, including structural support, metabolic support, insulation, and guidance of development. Primary tumors of the glial cells are called gliomas and often are malignant by the time they are diagnosed.
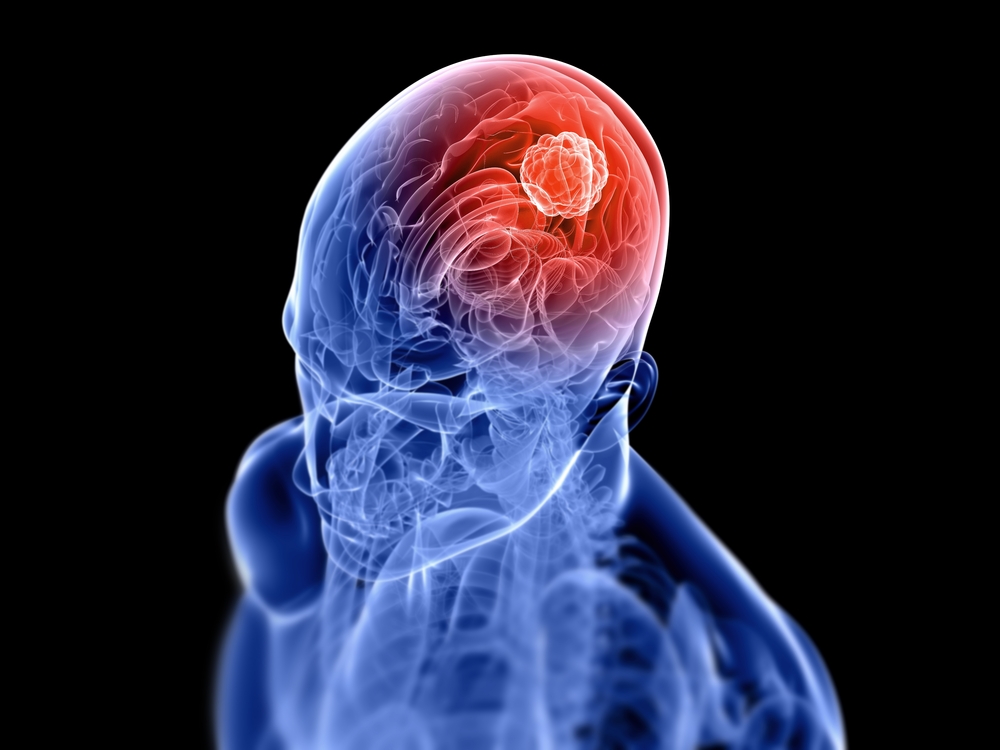
What is Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes.Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.
The most common primary brain tumors are:
Gliomas :
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. Gliomas comprise about 30 percent of all brain tumors and central nervous system tumours, and 80 percent of all malignant brain tumours.High-grade gliomas are highly vascular tumors and have a tendency to infiltrate diffusely. They have extensive areas of necrosis and hypoxia. Often, tumor growth causes a breakdown of the blood–brain barrier in the vicinity of the tumor. As a rule, high-grade gliomas almost always grow back even after complete surgical excision, so are commonly called recurrent cancer of the brain.Gliomas are classified by cell type, by grade, and by location.
Treatment for brain gliomas depends on the location, the cell type, and the grade of malignancy. Often, treatment is a combined approach, using surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. A prolonged survival was observed when treating with radiotherapy and concomitant temozolomide. Radiotherapy was given for 5 days a week for 6 week, with a total of 60 Gy. Temozolomide was given daily during the treatment of radiotherapy, at a dose of 75 mg per square meter of body surface area per day. When radiotherapy ended additionally six cycles of temozolomide were given, for five days during each cycle of 28 days.
The neoplasms currently referred to as meningiomata were referred to with a wide range of names in older medical literature, depending on the source. Various descriptors included “fungoid tumors”, “fungus of the dura mater”, “epithelioma”, “psammoma”, “dural sarcoma”, “dural endothelioma”, “fibrosarcoma”, “angioendothelioma”, “arachnoidal fibroboastoma”, “endotheliosis of the meninges”, “meningeal fibroblastoma”, “meningoblastoma”, “mestothelioma of the meninges”, “sarcoma of the dura”, and others
Meningiomata usually can be surgically resected (removed) and result in a permanent cure if the tumor is superficial on the dural surface and easily accessible. Transarterial embolization has become a standard preoperative procedure in the preoperative management. If invasion of the adjacent bone occurs, total removal is nearly impossible. It is rare for benign meningiomata to become malignant.
Meningiomas :
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur.
Meningiomata arise from arachnoidal cap cells, most of which are near the vicinity of the venous sinuses, and this is the site of greatest prevalence for meningioma formation. Some subtypes may arise from the pial cap cells that migrate during the development together with blood vessels into the brain parenchyma.
Pituitary adenomas:
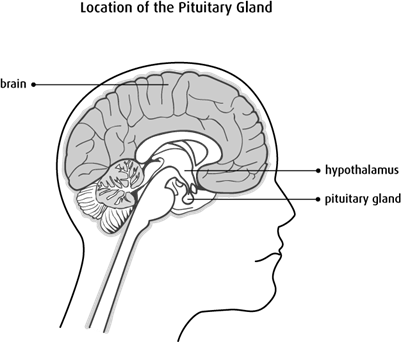
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is often referred to as the “master gland” of the human body. Part of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, it controls most of the body’s endocrine functions via the secretion of various hormones into the circulatory system. The pituitary gland is located below the brain in a depression (fossa) of the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica.
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Pituitary adenomas are generally divided into three categories dependent upon their biological functioning: benign adenoma, invasive adenoma, and carcinomas.Treatment options depend on the type of tumor and on its size.Pituitary incidentalomas are pituitary tumors that are characterized as an incidental finding. They are often discovered by computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), performed in the evaluation of unrelated medical conditions such as suspected head trauma, in cancer staging or in the evaluation of nonspecific symptoms such as dizziness and headache.
Nerve sheath tumors :
A nerve sheath tumor is a type of tumor of the nervous system (nervous system neoplasm) which is made up primarily of the myelin surrounding nerves.A peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST) is a nerve sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors include schwannomas and neurofibromas.A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a cancerous peripheral nerve sheath tumor.
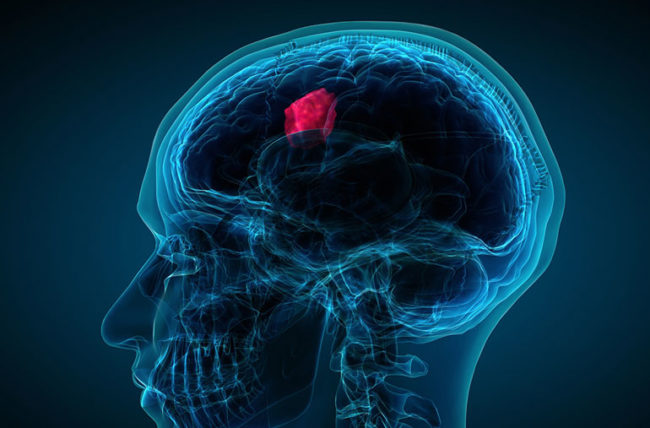
Brief introduction of other brain tumors :
Glioblastomas (GBMs):
are one of the most devastating primary tumors in humans and often results in minimal survival rates.Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most aggressive primary tumors in adults. Despite vigorous efforts and novel treatment approaches to reduce their impact on mortality, the median overall survival rate remains approximately 12–16 months.
Astrocytoma :
Astrocytomas are a type of brain tumor. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs.Astrocytoma causes regional effects by compression, invasion, and destruction of brain parenchyma, arterial and venous hypoxia, competition for nutrients, release of metabolic end products (e.g., free radicals, altered electrolytes, neurotransmitters), and release and recruitment of cellular mediators (e.g., cytokines) that disrupt normal parenchymal function.
There are no precise guidelines because the exact cause of astrocytoma is not known.For low-grade astrocytomas, removal of the tumor generally allows functional survival for many years. In some reports, the 5-year survival has been over 90% with well-resected tumors. Indeed, broad intervention of low-grade conditions is a contested matter. In particular, pilocytic astrocytomas are commonly indolent bodies that may permit normal neurologic function. However, left unattended, these tumors may eventually undergo neoplastic transformation.
Craniopharyngioma :
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak incidence rates are childhood-onset at 5–14 years and adult-onset at 50–74 years.Craniopharyngioma is a rare, usually suprasellar neoplasm, which may be cystic, that develops from nests of epithelium derived from Rathke’s pouch. Rathke’s pouch is an embryonic precursor of the anterior pituitary.
Craniopharyngiomas are almost always benign. However, as with many brain tumors, their treatment can be difficult, and significant morbidities are associated with both the tumor and treatment. Headache (obstructive hydrocephalus),
Hypersomnia,MyxedemaPostsurgical weight gain,Polydipsia,Polyuria (diabetes insipidus) ,Vision loss (bitemporal hemianopia).
Treatment generally consists of subfrontal or transsphenoidal excision. Endoscopic surgery through the noseoften performed by a joint team of neurosurgeons and ENT, is increasingly being considered as an alternative to transcranial surgery done by making an opening in the skull.Current research has shown ways of treating the tumors in a less invasive way while others have shown how the hypothalamus can be stimulated along with the tumor to prevent the child and adult with the tumor to become obese. Craniopharyngioma of childhood are commonly cystic in nature. Limited surgery minimizing hypothalamic damage may decrease the severe obesity rate at the expense of the need for radiotherapy to complete the treatment.
Brain tumors in infants
Brain tumors in infants have different clinical presentations, anatomical distribution, histopathological diagnosis, and clinical prognosis compared with older children.Brain tumors in infants should be treated with surgical resection, followed by chemotherapy when necessary.Central nervous system (CNS) tumors are among the most common neoplasms in children. Intracranial tumors with the onset of symptoms before the age of 1 year once were considered to be rare; however, increasing numbers of such tumors have been detected in recent decades thanks to widespread use of modern imaging techniques.
he histological distribution of malignant to benign brain tumors is higher in neonates (100%) and infants (53%) compared with older children (43%). According to a worldwide study by Di Rocco, the ten most common types of brain tumors in infancy are, in descending order, astrocytoma, medulloblastoma, ependymoma, choroid plexus papilloma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), teratoma, sarcoma, meningioma, ganglioglioma, and neuroblastoma.
According to the previous investigations, the survival among patients younger than 1 year of age was less than that of older patients. Poor prognosis and high mortality in this age group have been attributed to the risks of anesthesia, difficulty in postoperative care, lack of voluntary control of water and salt intake, and the biological behavior of tumor itself
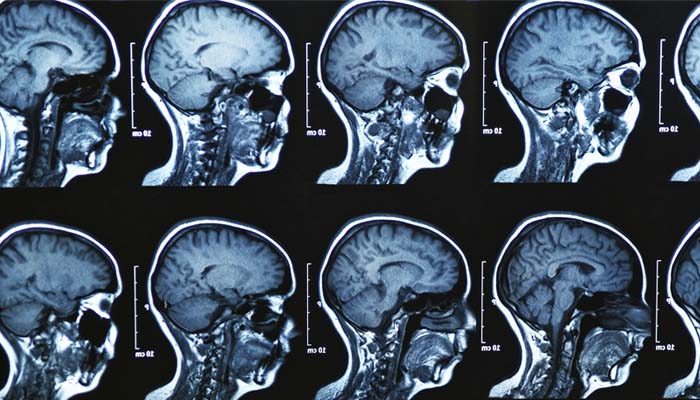
MRI :
Brain tumor patients often experience functional deficits that extend beyond the tumor site. While resting-state
functional MRI (rsfMRI) has been used to map such functional connectivity changes in brain tumor patients, the
interplay between abnormal tumor vasculature and the rsfMRI signal is still not well understood. Therefore,
there is an exigent need for new tools to elucidate how the blood‑oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) rsfMRI
signal is modulated in brain cancer. In this initial study, we explore the utility of a preclinical model for
quantifying brain tumor-induced changes on the rsfMRI signal and resting-state brain connectivity. We demonstrate that brain tumors induce brain-wide alterations of resting-state networks that extend to the contralateral hemisphere, accompanied by global attenuation of the rsfMRI signal. Preliminary histology suggests
that some of these alterations in brain connectivity may be attributable to tumor-related remodeling of the
neurovasculature. Moreover, this work recapitulates clinical rsfMRI findings from brain tumor patients in terms
of the effects of tumor size on the neurovascular microenvironment. Collectively, these results lay the foundation
of a preclinical platform for exploring the usefulness of rsfMRI as a potential new biomarker in patients with
brain cancer.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can generate mass amounts of data within a narrow time frame. Furthermore, it is safer than and not as invasive as other imaging techniques . The most popular areas for examination have been the spine and head, over the last ten years. In fact, more than half of the MRI scans have been concentrated on these areas of the body. Disorders of the central nervous system, backbone, and spine have been commonly analyzed with this technique, as well as cardiovascular system diseases and disorders of the extremities.
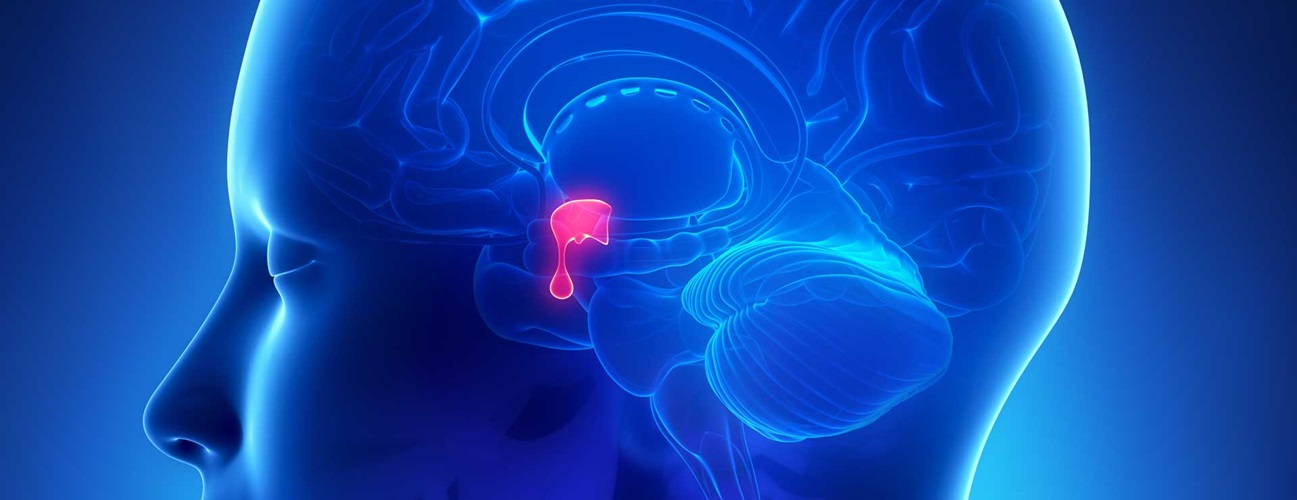
by best-mag | medicine
The pituitary gland (PG) is said to be a “master” endocrine gland and through its tropic hormones influences other endocrine glands to secrete hormones that have a variety of effects on body systems.The anatomist Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring coined the name hypophysis.This name consists of ὑπό (‘under’) and φύειν (‘to grow’). In later Greek ὑπόφυσις is used differently by Greek physicians as outgrowth. Sömmering also used the equivalent expression appendix cerebri, with appendix as appendage. In various languages, Hirnanhang in German and hersenaanhangsel in Dutch, the terms are derived from appendix cerebri.
The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume o pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm.
The pituitary gland, in humans, is oval in shape and is a pea-sized gland that sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica. It is composed of two lobes: anterior and posterior, with the intermediate lobe that joins the two regions. In many animals, these three lobes are distinct. The intermediate is avascular and almost absent in human beings. The intermediate lobe is present in many animal species, in particular in rodents, mice and rats, that have been used extensively to study pituitary development and function. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pituitary is distinct from the neural composition of the posterior pituitary, which is an extension of the hypothalamus.
Pituitary gland anatomy :
The pituitary gland is within the sella turcica or the hypophyseal fossa. This structure is present near the center at the base of the cranium and is fibro-osseous. The anatomical boundaries of the gland have clinical and surgical significance. Sella turcica is a concave indentation in the sphenoid bone.
In most species the pituitary gland is divided into three lobes: the anterior lobe, the intermediate lobe, and the posterior lobe (also called the neurohypophysis or pars nervosa).
pituitary gland Hormones :
Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help control the following body processes:
Growth (GH)
Blood pressure
Some aspects of pregnancy and childbirth including stimulation of uterine contractions
Breast milk production
Sex organ functions in both sexes
Thyroid gland function
Metabolic conversion of food into energy
Water and osmolarity regulation in the body
Water balance via the control of reabsorption of water by the kidneys
Temperature regulation
Pain relief
The pituitary gland is found in all vertebrates, but its structure varies among different groups.The intermediate lobe is, in general, not well developed in tetrapods, and is entirely absent in birds.
pituitary insufficiency:
Hypopituitarism (also called pituitary insufficiency) is a rare condition in which the pituitary gland doesn’t make enough of certain hormones. Hypopituitarism can develop suddenly after surgery, injury, or bleeding, or very slowly, over several months or even over several years.
pituitary insufficiency symptoms: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency . Severe fatigue. Low blood pressure, which may lead to fainting. Frequent and prolonged infections. Nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain
Pituitary gland tumor:
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths that develop in your pituitary gland. Some pituitary tumors result in too much of the hormones that regulate important functions of your body. Some pituitary tumors can cause your pituitary gland to produce lower levels of hormones.Pituitary cancer is very rare. Still, the tumors can cause serious problems, either because of their size (large tumors) or because they make extra hormones your body doesn’t need (functioning tumors). They’re typically treated with surgery, medicine, or radiation
Pituitary gland for Frequently Asked Questions ؟
What is function of pituitary gland?
Your pituitary gland is an important pea-sized organ. If your pituitary gland doesn’t function properly, it affects vital parts like your brain, skin, energy, mood, reproductive organs, vision, growth and more. It’s the “master” gland because it tells other glands to release hormones.
Can you live without a pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is called the master gland of the endocrine system. This is because it controls many other hormone glands in the body. According to The Pituitary Foundation, without it, the body wouldn’t reproduce, wouldn’t grow properly and many other bodily functions just wouldn’t function.
How can I improve my pituitary function?
eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which are great sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.choosing good sources of fats, such as those that contain omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fats.
What are pituitary symptoms?
Change hormone production, leading to symptoms such as weight gain, stunted or excessive growth, high blood pressure, low sex drive or mood changes. Press against the pituitary gland, optic nerves or brain tissue, causing vision problems or headaches.
Is a pituitary tumor serious?
Pituitary cancer is very rare. Still, the tumors can cause serious problems, either because of their size (large tumors) or because they make extra hormones your body doesn’t need (functioning tumors). They’re typically treated with surgery, medicine, or radiation.
Is pituitary tumor curable?
Most pituitary tumors are curable. If a pituitary tumor is diagnosed early, the outlook for recovery is usually excellent. However, if tumors grow large enough, or grow rapidly, they are more likely to cause problems and will be more difficult to treat.





















