by best-mag | medicine
The brains of humans and other vertebrates are composed of very soft tissue and have a gelatin-like texture. Living brain tissue has a pink tint in color on the outside (gray matter), and nearly complete white on the inside (white matter), with subtle variations in color. The three largest divisions of the brain are:
Cerebral cortex
Brainstem
Cerebellum
These areas are composed of two broad classes of cells: neurons and glia. These two types are equally numerous in the brain as a whole, although glial cells outnumber neurons roughly 4 to 1 in the cerebral cortex. Glia come in several types, which perform a number of critical functions, including structural support, metabolic support, insulation, and guidance of development. Primary tumors of the glial cells are called gliomas and often are malignant by the time they are diagnosed.
What is Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes.Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.
The most common primary brain tumors are:
Gliomas :
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. Gliomas comprise about 30 percent of all brain tumors and central nervous system tumours, and 80 percent of all malignant brain tumours.High-grade gliomas are highly vascular tumors and have a tendency to infiltrate diffusely. They have extensive areas of necrosis and hypoxia. Often, tumor growth causes a breakdown of the blood–brain barrier in the vicinity of the tumor. As a rule, high-grade gliomas almost always grow back even after complete surgical excision, so are commonly called recurrent cancer of the brain.Gliomas are classified by cell type, by grade, and by location.
Treatment for brain gliomas depends on the location, the cell type, and the grade of malignancy. Often, treatment is a combined approach, using surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. A prolonged survival was observed when treating with radiotherapy and concomitant temozolomide. Radiotherapy was given for 5 days a week for 6 week, with a total of 60 Gy. Temozolomide was given daily during the treatment of radiotherapy, at a dose of 75 mg per square meter of body surface area per day. When radiotherapy ended additionally six cycles of temozolomide were given, for five days during each cycle of 28 days.
The neoplasms currently referred to as meningiomata were referred to with a wide range of names in older medical literature, depending on the source. Various descriptors included “fungoid tumors”, “fungus of the dura mater”, “epithelioma”, “psammoma”, “dural sarcoma”, “dural endothelioma”, “fibrosarcoma”, “angioendothelioma”, “arachnoidal fibroboastoma”, “endotheliosis of the meninges”, “meningeal fibroblastoma”, “meningoblastoma”, “mestothelioma of the meninges”, “sarcoma of the dura”, and others
Meningiomata usually can be surgically resected (removed) and result in a permanent cure if the tumor is superficial on the dural surface and easily accessible. Transarterial embolization has become a standard preoperative procedure in the preoperative management. If invasion of the adjacent bone occurs, total removal is nearly impossible. It is rare for benign meningiomata to become malignant.
Meningiomas :
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur.
Meningiomata arise from arachnoidal cap cells, most of which are near the vicinity of the venous sinuses, and this is the site of greatest prevalence for meningioma formation. Some subtypes may arise from the pial cap cells that migrate during the development together with blood vessels into the brain parenchyma.
Pituitary adenomas:
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is often referred to as the “master gland” of the human body. Part of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, it controls most of the body’s endocrine functions via the secretion of various hormones into the circulatory system. The pituitary gland is located below the brain in a depression (fossa) of the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica.
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Pituitary adenomas are generally divided into three categories dependent upon their biological functioning: benign adenoma, invasive adenoma, and carcinomas.Treatment options depend on the type of tumor and on its size.Pituitary incidentalomas are pituitary tumors that are characterized as an incidental finding. They are often discovered by computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), performed in the evaluation of unrelated medical conditions such as suspected head trauma, in cancer staging or in the evaluation of nonspecific symptoms such as dizziness and headache.
Nerve sheath tumors :
A nerve sheath tumor is a type of tumor of the nervous system (nervous system neoplasm) which is made up primarily of the myelin surrounding nerves.A peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST) is a nerve sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors include schwannomas and neurofibromas.A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a cancerous peripheral nerve sheath tumor.
Brief introduction of other brain tumors :
Glioblastomas (GBMs):
are one of the most devastating primary tumors in humans and often results in minimal survival rates.Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most aggressive primary tumors in adults. Despite vigorous efforts and novel treatment approaches to reduce their impact on mortality, the median overall survival rate remains approximately 12–16 months.
Astrocytoma :
Astrocytomas are a type of brain tumor. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs.Astrocytoma causes regional effects by compression, invasion, and destruction of brain parenchyma, arterial and venous hypoxia, competition for nutrients, release of metabolic end products (e.g., free radicals, altered electrolytes, neurotransmitters), and release and recruitment of cellular mediators (e.g., cytokines) that disrupt normal parenchymal function.
There are no precise guidelines because the exact cause of astrocytoma is not known.For low-grade astrocytomas, removal of the tumor generally allows functional survival for many years. In some reports, the 5-year survival has been over 90% with well-resected tumors. Indeed, broad intervention of low-grade conditions is a contested matter. In particular, pilocytic astrocytomas are commonly indolent bodies that may permit normal neurologic function. However, left unattended, these tumors may eventually undergo neoplastic transformation.
Craniopharyngioma :
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak incidence rates are childhood-onset at 5–14 years and adult-onset at 50–74 years.Craniopharyngioma is a rare, usually suprasellar neoplasm, which may be cystic, that develops from nests of epithelium derived from Rathke’s pouch. Rathke’s pouch is an embryonic precursor of the anterior pituitary.
Craniopharyngiomas are almost always benign. However, as with many brain tumors, their treatment can be difficult, and significant morbidities are associated with both the tumor and treatment. Headache (obstructive hydrocephalus),
Hypersomnia,MyxedemaPostsurgical weight gain,Polydipsia,Polyuria (diabetes insipidus) ,Vision loss (bitemporal hemianopia).
Treatment generally consists of subfrontal or transsphenoidal excision. Endoscopic surgery through the noseoften performed by a joint team of neurosurgeons and ENT, is increasingly being considered as an alternative to transcranial surgery done by making an opening in the skull.Current research has shown ways of treating the tumors in a less invasive way while others have shown how the hypothalamus can be stimulated along with the tumor to prevent the child and adult with the tumor to become obese. Craniopharyngioma of childhood are commonly cystic in nature. Limited surgery minimizing hypothalamic damage may decrease the severe obesity rate at the expense of the need for radiotherapy to complete the treatment.
Brain tumors in infants
Brain tumors in infants have different clinical presentations, anatomical distribution, histopathological diagnosis, and clinical prognosis compared with older children.Brain tumors in infants should be treated with surgical resection, followed by chemotherapy when necessary.Central nervous system (CNS) tumors are among the most common neoplasms in children. Intracranial tumors with the onset of symptoms before the age of 1 year once were considered to be rare; however, increasing numbers of such tumors have been detected in recent decades thanks to widespread use of modern imaging techniques.
he histological distribution of malignant to benign brain tumors is higher in neonates (100%) and infants (53%) compared with older children (43%). According to a worldwide study by Di Rocco, the ten most common types of brain tumors in infancy are, in descending order, astrocytoma, medulloblastoma, ependymoma, choroid plexus papilloma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), teratoma, sarcoma, meningioma, ganglioglioma, and neuroblastoma.
According to the previous investigations, the survival among patients younger than 1 year of age was less than that of older patients. Poor prognosis and high mortality in this age group have been attributed to the risks of anesthesia, difficulty in postoperative care, lack of voluntary control of water and salt intake, and the biological behavior of tumor itself
MRI :
Brain tumor patients often experience functional deficits that extend beyond the tumor site. While resting-state
functional MRI (rsfMRI) has been used to map such functional connectivity changes in brain tumor patients, the
interplay between abnormal tumor vasculature and the rsfMRI signal is still not well understood. Therefore,
there is an exigent need for new tools to elucidate how the blood‑oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) rsfMRI
signal is modulated in brain cancer. In this initial study, we explore the utility of a preclinical model for
quantifying brain tumor-induced changes on the rsfMRI signal and resting-state brain connectivity. We demonstrate that brain tumors induce brain-wide alterations of resting-state networks that extend to the contralateral hemisphere, accompanied by global attenuation of the rsfMRI signal. Preliminary histology suggests
that some of these alterations in brain connectivity may be attributable to tumor-related remodeling of the
neurovasculature. Moreover, this work recapitulates clinical rsfMRI findings from brain tumor patients in terms
of the effects of tumor size on the neurovascular microenvironment. Collectively, these results lay the foundation
of a preclinical platform for exploring the usefulness of rsfMRI as a potential new biomarker in patients with
brain cancer.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can generate mass amounts of data within a narrow time frame. Furthermore, it is safer than and not as invasive as other imaging techniques . The most popular areas for examination have been the spine and head, over the last ten years. In fact, more than half of the MRI scans have been concentrated on these areas of the body. Disorders of the central nervous system, backbone, and spine have been commonly analyzed with this technique, as well as cardiovascular system diseases and disorders of the extremities.

by best-mag | Cryptocurrency
Shiba Inu token is a decentralized cryptocurrency created in August 2020 by an anonymous person or group known as “Ryoshi”.It is a meme coin launched as a rival of Dogecoin or “Doge-Killer”.Well, Shiba Inu has been one of the best performing cryptocurrencies of 2021. It is still one of the top #15 largest cryptocurrencies by marketcap.
It is named after the Shiba Inu (柴犬), a Japanese breed of dog originating in the Chūbu region, the same breed that is depicted in Dogecoin’s symbol, itself originally a satirical cryptocurrency based on the Doge meme.
While Shiba Inu was first known as an alternative to Dogecoin, it has a key difference. Shiba Inu is built on the Ethereum (CRYPTO:ETH) blockchain, so it can run smart contracts. Through smart contracts, Shiba Inu can work with decentralized applications.
From its inception, Shiba Inu has done things differently. Starting with a supply of 1 quadrillion, our founder, Ryoshi, locked 50% in Uniswap, then “burned” the other half to Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin for safekeeping.

The Shiba Inu token is our foundational currency that allows investors to hold millions, billions, or even trillions, of it in their wallets. Between its international recognition and its legitimate utility, SHIB is up thousands of times and is constantly expanding its reach. SHIB is the first to be listed and incentivized on ShibaSwap, our proprietary DEX.SHIB, LEASH, and BONE, come together to create ShibaSwap, the next evolution in DeFi platforms. ShibaSwap gives users the ability to DIG (provide liquidity), BURY (stake), and SWAP tokens to gain WOOF Returns through our sophisticated and innovative passive income reward system.
Liquidity Locked to Uniswap
India’s Covid Relief Fund
Vitalik Buterin Burn
This meme coin quickly gained speed and value as a community of investors was drawn in by the cute charm of the coin paired with headlines and tweets from personalities like Elon Musk and Vitalik Buterin. Vitalik Buterin was long believed to be the originator of Shiba Inu, but denied such rumors on the Lex Fridman podcast on June 5, 2021.
Shiba’s success sparked an avalanche of copycats, such as BitShiba, Shiba Fantom, Shibalana, King Shiba, SHIBAVAX, Captain Shibarrow, SHIBA2K22, SpookyShiba and countless others. In total, there may be well over 100 Shiba Inu copies, and the number keeps rising constantly.
shiba inu Frequently Asked Questions :
Who Are the Founders of SHIBA INU?
The anonymous creator of the Shiba Inu coin is known as “Ryoshi.” However, very little is known of the mystery founder of the dog-themed cryptocurrency, much like the founder of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto.According to Ryoshi, the end goal is that SHI becomes a global stable currency “that plebs across all countries are able to use as both a store of value and method of payment.”
Is Shiba Inu a coin or token?
If you still don’t know Shiba Inu, it is an Ethereum-based altcoin or meme coin that features the Japanese dog breed Shiba Inu as its mascot.
Is Shiba Inu the same as Dogecoin?
The tale of two dog-themed coins , Both DOGE and SHIB were created as a joke, and they have the same dog, a Shiba Inu, for a mascot. However, this is where the similarities end. Dogecoin: DOGE was created in 2013 by engineers Billy Markus, then an employee at IBM, and Jackson Palmer from Adobe.
what do token burns do ?
“Burning” crypto means permanently removing a number of tokens from circulation. This is typically done by transferring the tokens in question to a burn address, i.e. a wallet from which they cannot ever be retrieved. This is often described as destroying tokens. A project burns its tokens to reduce the overall supply.
Does Shiba Inu burn tokens?
Shibburn is created for Shiba investors to burn their tokens. In the platform, burns are calculated using three special addresses, two dead wallets, which have no obtainable keys, and tokens sent to the Genesis address to reduce the supply.
Why do Shiba tokens burn?
This is an important moment for the Shiba Inu community or commonly known as ShibArmy to strengthen the token project. For information, burning or burning coins is an effort to reduce the supply of coins from circulation. Usually the burning also boosts the value of the burned coins as did Ethereum some time ago.
Does Shiba Inu coin have a future?
Most experts agree that the Shiba Inu token has a future, as it has active support from the community. If the Shiba Inu price continues to rise at its current rate, it will be an incredibly worthwhile investment.
How many Shibusd are there?
394 trillion SHIB
Shiba Inu website ?
https://shibatoken.com
Shiba Inu Price Prediction 2022 ?
Shiba Inu Price History ,Shiba Inu was launched on August 1, 2020. The price of 1 unit of the asset cost $0.00000000051. At the time $100, was 196,078,431,372 SHIB. But, Shiba Inu broke into the limelight in April 2021 with the markets’ historic high at the time. This created a perfect opportunity for the self-proclaimed “Dogecoin killer” to thrive. Since then Shiba Inu has become known as one of the most undervalued cryptos on the market.
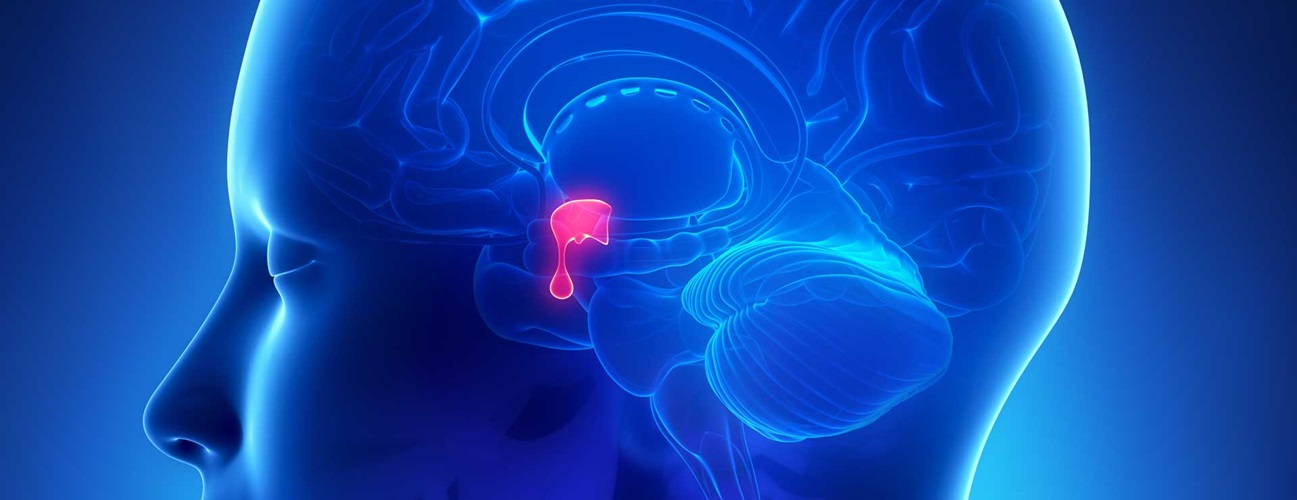
by best-mag | medicine
The pituitary gland (PG) is said to be a “master” endocrine gland and through its tropic hormones influences other endocrine glands to secrete hormones that have a variety of effects on body systems.The anatomist Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring coined the name hypophysis.This name consists of ὑπό (‘under’) and φύειν (‘to grow’). In later Greek ὑπόφυσις is used differently by Greek physicians as outgrowth. Sömmering also used the equivalent expression appendix cerebri, with appendix as appendage. In various languages, Hirnanhang in German and hersenaanhangsel in Dutch, the terms are derived from appendix cerebri.
The height of the pituitary gland ranges from 5.3 to 7.0 mm. The volume o pituitary gland ranges from 200 to 440 mm.
The pituitary gland, in humans, is oval in shape and is a pea-sized gland that sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica. It is composed of two lobes: anterior and posterior, with the intermediate lobe that joins the two regions. In many animals, these three lobes are distinct. The intermediate is avascular and almost absent in human beings. The intermediate lobe is present in many animal species, in particular in rodents, mice and rats, that have been used extensively to study pituitary development and function. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pituitary is distinct from the neural composition of the posterior pituitary, which is an extension of the hypothalamus.
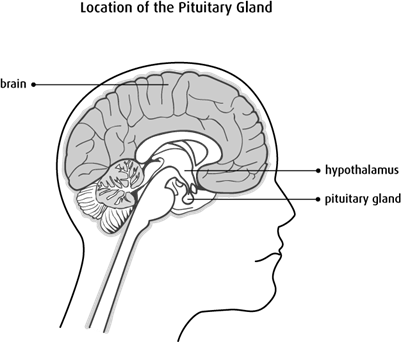
Pituitary gland anatomy :
The pituitary gland is within the sella turcica or the hypophyseal fossa. This structure is present near the center at the base of the cranium and is fibro-osseous. The anatomical boundaries of the gland have clinical and surgical significance. Sella turcica is a concave indentation in the sphenoid bone.
In most species the pituitary gland is divided into three lobes: the anterior lobe, the intermediate lobe, and the posterior lobe (also called the neurohypophysis or pars nervosa).
pituitary gland Hormones :
Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help control the following body processes:
Growth (GH)
Blood pressure
Some aspects of pregnancy and childbirth including stimulation of uterine contractions
Breast milk production
Sex organ functions in both sexes
Thyroid gland function
Metabolic conversion of food into energy
Water and osmolarity regulation in the body
Water balance via the control of reabsorption of water by the kidneys
Temperature regulation
Pain relief
The pituitary gland is found in all vertebrates, but its structure varies among different groups.The intermediate lobe is, in general, not well developed in tetrapods, and is entirely absent in birds.
pituitary insufficiency:
Hypopituitarism (also called pituitary insufficiency) is a rare condition in which the pituitary gland doesn’t make enough of certain hormones. Hypopituitarism can develop suddenly after surgery, injury, or bleeding, or very slowly, over several months or even over several years.
pituitary insufficiency symptoms: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency . Severe fatigue. Low blood pressure, which may lead to fainting. Frequent and prolonged infections. Nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain
Pituitary gland tumor:
Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths that develop in your pituitary gland. Some pituitary tumors result in too much of the hormones that regulate important functions of your body. Some pituitary tumors can cause your pituitary gland to produce lower levels of hormones.Pituitary cancer is very rare. Still, the tumors can cause serious problems, either because of their size (large tumors) or because they make extra hormones your body doesn’t need (functioning tumors). They’re typically treated with surgery, medicine, or radiation
Pituitary gland for Frequently Asked Questions ؟
What is function of pituitary gland?
Your pituitary gland is an important pea-sized organ. If your pituitary gland doesn’t function properly, it affects vital parts like your brain, skin, energy, mood, reproductive organs, vision, growth and more. It’s the “master” gland because it tells other glands to release hormones.
Can you live without a pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is called the master gland of the endocrine system. This is because it controls many other hormone glands in the body. According to The Pituitary Foundation, without it, the body wouldn’t reproduce, wouldn’t grow properly and many other bodily functions just wouldn’t function.
How can I improve my pituitary function?
eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which are great sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.choosing good sources of fats, such as those that contain omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fats.
What are pituitary symptoms?
Change hormone production, leading to symptoms such as weight gain, stunted or excessive growth, high blood pressure, low sex drive or mood changes. Press against the pituitary gland, optic nerves or brain tissue, causing vision problems or headaches.
Is a pituitary tumor serious?
Pituitary cancer is very rare. Still, the tumors can cause serious problems, either because of their size (large tumors) or because they make extra hormones your body doesn’t need (functioning tumors). They’re typically treated with surgery, medicine, or radiation.
Is pituitary tumor curable?
Most pituitary tumors are curable. If a pituitary tumor is diagnosed early, the outlook for recovery is usually excellent. However, if tumors grow large enough, or grow rapidly, they are more likely to cause problems and will be more difficult to treat.

by best-mag | Cooking
French cuisine consists of the cooking traditions and practices from France. French cuisine developed throughout the centuries influenced by the many surrounding cultures of Spain, Italy, Switzerland, …
Fresh, naturally produced ingredients can always be found in French cuisine. cheese, olive oil, and seasonal vegetables are just a few staples. Herbs and spices are also important to French cuisine and can contribute a depth of flavor to otherwise subtle dishes
1.Soufflé

A soufflé is a baked egg-based dish originating in France in the early eighteenth century. Combined with various other ingredients it can be served as a savory main dish or sweetened as a dessert.
The soufflé earns its name from the French word soufflér — to puff. It was perfected in the mid-1800s by Marie-Antoine Carême who, in cooking for the newly rich in Paris, was aided by updated ovens that were heated by air drafts rather than coal. This change was key to the rise of the soufflé.
PB Soufflé, aka Peanut Butter Soufflé, is an offspring of the sweet Do-Si-Dos and Lava Cake strains. This indica strain lives up to its name with a delicious chocolaty, herbal flavor that’s accented by spicy cookies upon exhale.
Any ovenproof pan with deep, preferably straight sides can work as a souffle pan substitute.
10 Types of Soufflé Sorted by Popularity :
Soufflé au chocolat
Soufflé au fromage
Soufflé aux épinards
Soufflé au citron
Grand Marnier Souffle
Soufflé aux framboises
Soufflé glacé
Soufflé aux carottes
Pommes de terre soufflées
Soufflé au poulet
2.Coq au vin

Coq au vin is a French dish of chicken braised with wine, lardons, mushrooms, and optionally garlic. A red Burgundy wine is typically used, though many regions of France make variants using local wines, such as coq au vin jaune, coq au riesling, coq au pourpre or coq au violet, coq au Champagne, etc.
Various legends trace coq au vin to ancient Gaul and Julius Caesar, but the recipe was not documented until the early 20th century; it is generally accepted that it existed as a rustic dish long before that. A somewhat similar recipe, poulet au vin blanc, appeared in an 1864 cookbook.
Julia Child included coq au vin in her 1961 cookbook Mastering the Art of French Cooking, and she prepared it twice on the PBS cooking show The French Chef. This exposure helped to increase the visibility and popularity of the dish in the United States, and coq au vin was seen as one of Child’s signature dishes.
Main ingredients: Chicken, wine, lardons, mushrooms, optionally garlic
3.Beef bourguignon

Beef bourguignon or bœuf bourguignon, also called beef Burgundy, and bœuf à la Bourguignonne, is a French beef stew braised in red wine, often red Burgundy, and beef stock, typically flavored with carrots, onions, garlic, and a bouquet garni, and garnished with pearl onions, mushrooms, and bacon.
Main ingredients: Beef, red wine (often red Burgundy), beef stock, lardons, onions, bouquet garni, pearl onions, mushrooms
The dish is often “touted as traditional”, but it was first documented in 1867, and “does not appear to be very old”. Other recipes called “à la Bourguignonne” with similar garnishes are found in the mid-19th century for leg of lamb and for rabbit. In the 19th century, it “did not enjoy a great reputation”, perhaps because it was often made with leftover cooked meat.The dish has become a standard of French cuisine, notably in Parisian bistrots; however, it only began to be considered as a Burgundian specialty in the twentieth century.
Julia Child has described the dish as “certainly one of the most delicious beef dishes concocted by man”.
Alternative names: Beef Burgundy, bœuf à la bourguignonne
Beef bourguignon is generally accompanied with boiled potatoes or pasta.
4.French onion soup (Soupe à l’oignon)

French onion soup is a soup usually based on meat stock and onions, and often served gratinéed with croutons or a larger piece of bread covered with cheese floating on top. Ancient in origin, the dish underwent a resurgence of popularity in the 1960s in the United States due to a greater interest in French cuisine.
Onion soups have been popular at least as far back as Roman times. Throughout history, they were seen as food for poor people, as onions were plentiful and easy to grow. The modern version of this soup originates in Paris, France in the 18th century, made from beef broth, and caramelized onions.
It was introduced to the United States by the New York restaurant of Henri Mouquin in 1861, where his wife Marie Julie Grandjean Mouquin was the chef. It is often finished by being placed under a salamander in a ramekin with croutons and Comté melted on top. The crouton on top is reminiscent of ancient soups (see history of soup).
5.Cassoulet
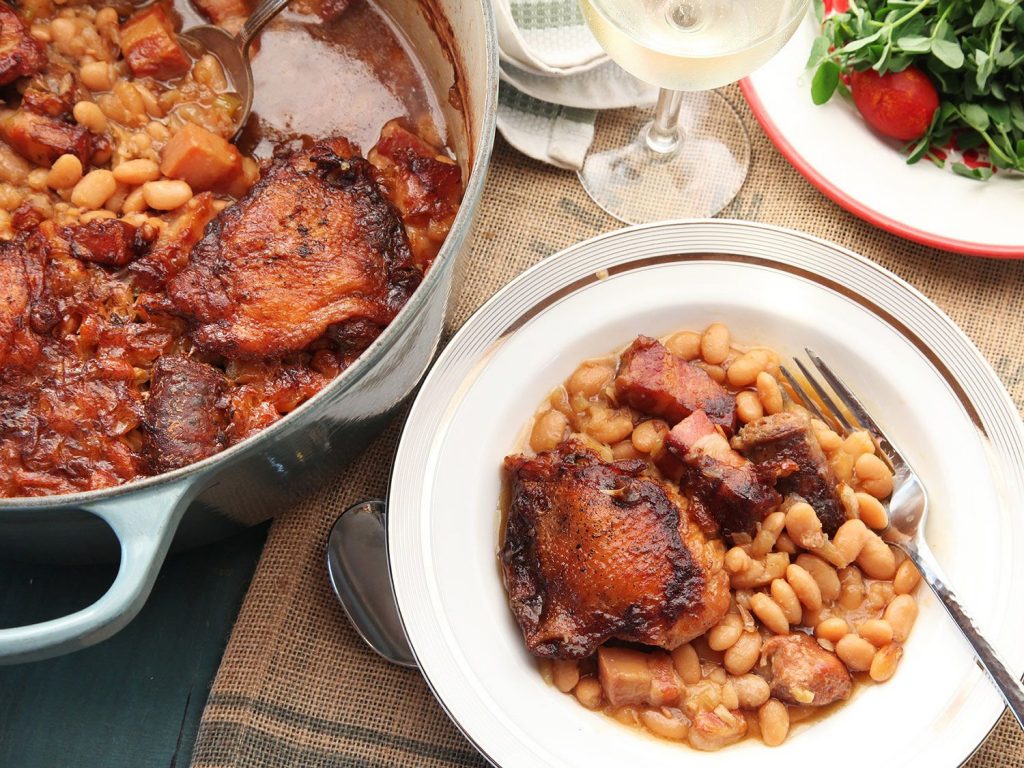

Cassoulet is a rich, slow-cooked casserole containing meat, pork skin and white beans, originating in southern France. It is named after its traditional cooking vessel, the casserole, a deep, round, earthenware pot with slanting sides.
In France, cassoulets of varying price and quality are also sold in cans and jars in supermarkets, grocery stores, and delicatessens. The cheapest ones contain only beans, tomato sauce, sausages, and bacon. More expensive versions are likely to be cooked with goose fat and to include Toulouse sausages, lamb, goose, or duck confit.
Main ingredients: Meat (typically pork sausages, goose, duck, sometimes mutton), pork skin, white haricot beans
6.Ratatouille
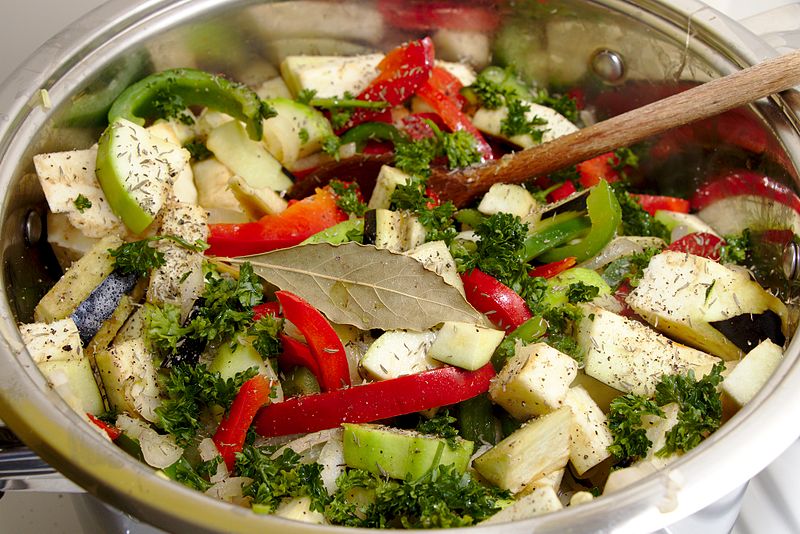

Ratatouille. Recipes and cooking times differ widely, but common ingredients include tomato, garlic, onion, courgette (zucchini), aubergine (eggplant), capsicum (bell pepper), and some combination of leafy green herbs common to the region
The Guardian’s food and drink writer, Felicity Cloake, wrote in 2016 that, considering ratatouille’s relatively recent origins (it first appeared in 1877), there exists a great variety of methods of preparation for it. The Larousse Gastronomique claims “according to the purists, the different vegetables should be cooked separately, then combined and cooked slowly together until they attain a smooth, creamy consistency”, so that (according to the chair of the Larousse’s committee Joël Robuchon) “each [vegetable] will taste truly of itself.”
7.Salad Nicoise (Salade niçoise)
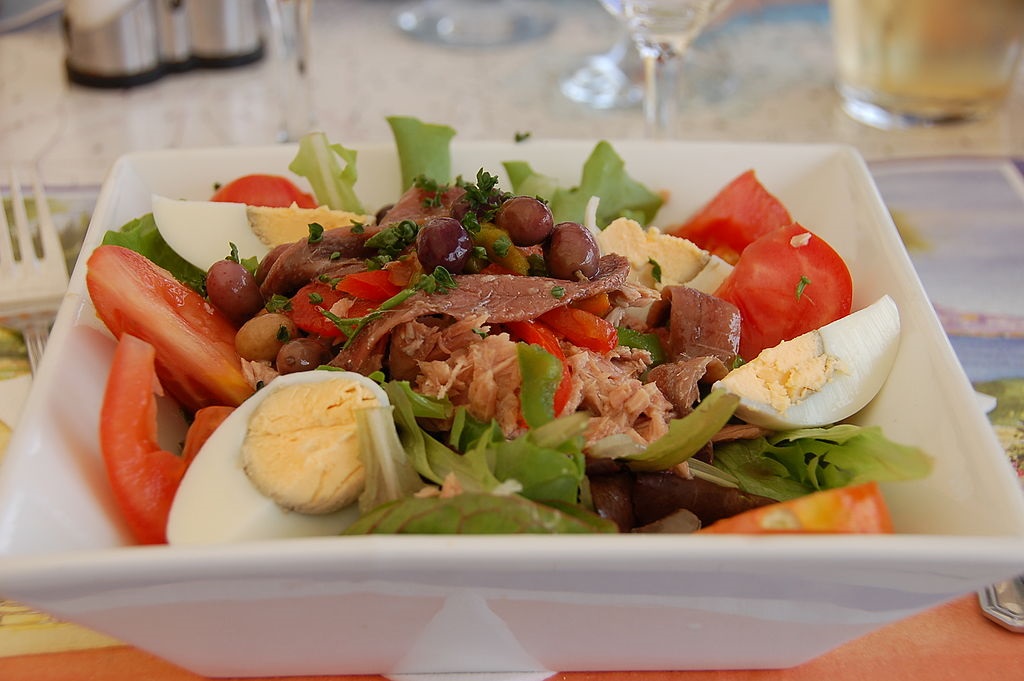

Salade niçoise, salada nissarda in the Niçard dialect of the Occitan language, insalata nizzarda in Italian, is a salad that originated in the French city of Nice.
The question of the proper ingredients appropriate for a salade niçoise has long been the subject of debate and even controversy. The British cook Nigella Lawson observed “Everyone seems to have a very strong opinion as to what should or should not go into a Salade Niçoise”. Chef and cookbook author Auguste Escoffier (1846–1935), born in Villeneuve-Loubet near Nice, added potatoes and green beans, an innovation that remains controversial as a “questionable idea” a century later.
8.Flamiche

Flamiche is a specialty of Picardy, and a puff pastry tart made with leeks and cream. The pastry is made of a brioche-type dough. It resembles a quiche.
Flamiche is a specialty of Picardy (located in northern France), and a puff pastry tart made with leeks and cream. The pastry is made of a brioche-typedough. It resembles a quiche. It is also a speciality of Dinant and of Walloon cuisine, a tart made from a base of low-fat cheese (boulette de Romedenne) butter and eggs, is eaten hot

by best-mag | Cryptocurrency
In 2009, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, bitcoin, was created by presumably pseudonymous developer Satoshi Nakamoto. It used SHA-256, a cryptographic hash function, in its proof-of-work scheme.In April 2011, Namecoin was created as an attempt at forming a decentralized DNS, which would make internet censorship very difficult. Soon after, in October 2011, Litecoin was released. It used scrypt as its hash function instead of SHA-256. Another notable cryptocurrency, Peercoin, used a proof-of-work/proof-of-stake hybrid.
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Cryptocurrency, sometimes called crypto-currency or crypto, is any form of currency that exists digitally or virtually and uses cryptography to secure transactions. Cryptocurrencies don’t have a central issuing or regulating authority, instead using a decentralized system to record transactions and issue new units.A cryptocurrency is an encrypted data string that denotes a unit of currency. It is monitored and organized by a peer-to-peer network called a blockchain, which also serves as a secure ledger of transactions, e.g., buying, selling, and transferring.
Cryptocurrency does not exist in physical form (like paper money) and is typically not issued by a central authority. Cryptocurrencies typically use decentralized control as opposed to a central bank digital currency (CBDC). When a cryptocurrency is minted or created prior to issuance or issued by a single issuer, it is generally considered centralized. When implemented with decentralized control, each cryptocurrency works through distributed ledger technology, typically a blockchain, that serves as a public financial transaction database.
What Altcoins ?
Tokens, cryptocurrencies, and other types of digital assets that are not bitcoin are collectively known as alternative cryptocurrencies,typically shortened to “altcoins” or “alt coins”,or disparagingly known as “shitcoins”. Paul Vigna of The Wall Street Journal also described altcoins as “alternative versions of bitcoin” given its role as the model protocol for altcoin designers. The term is commonly used to describe coins and tokens created after bitcoin.Altcoins often have underlying differences with bitcoin. For example, Litecoin aims to process a block every 2.5 minutes, rather than bitcoin’s 10 minutes, which allows Litecoin to confirm transactions faster than bitcoin. Another example is Ethereum, which has smart contract functionality that allows decentralized applications to be run on its blockchain. Ethereum was the most used blockchain in 2020, according to Bloomberg News. In 2016, it had the largest “following” of any altcoin, according to the New York Times.
What altseason ?
Significant rallies across altcoin markets are often referred to as an “altseason”.
What Mining (Hashcoin mine) ?
In cryptocurrency networks, mining is a validation of transactions. For this effort, successful miners obtain new cryptocurrency as a reward. The reward decreases transaction fees by creating a complementary incentive to contribute to the processing power of the network. The rate of generating hashes, which validate any transaction, has been increased by the use of specialized machines such as FPGAs and ASICs running complex hashing algorithms like SHA-256 and scrypt. This arms race for cheaper-yet-efficient machines has existed since the first cryptocurrency, bitcoin, was introduced in 2009.
What Wallets ?
A cryptocurrency wallet stores the public and private “keys” (address) or seed which can be used to receive or spend the cryptocurrency.With the private key, it is possible to write in the public ledger, effectively spending the associated cryptocurrency. With the public key, it is possible for others to send currency to the wallet.
There exist multiple methods of storing keys or seed in a wallet from using paper wallets which are traditional public, private or seed keys written on paper to using hardware wallets which are dedicated hardware to securely store your wallet information, using a digital wallet which is a computer with a software hosting your wallet information, hosting your wallet using an exchange where cryptocurrency is traded. or by storing your wallet information on a digital medium such as plaintext.
What Cryptocurrency exchange ?
A cryptocurrency exchange, or a digital currency exchange (DCE), is a business that allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets, such as conventional fiat money or other digital currencies. Exchanges may accept credit card payments, wire transfers or other forms of payment in exchange for digital currencies or cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency exchange can be a market maker that typically takes the bid–ask spreads as a transaction commission for is service or, as a matching platform, simply charges fees.
What Cryptocurrency trading ?
Cryptocurrency trading is the act of speculating on cryptocurrency price movements via a CFD trading account, or buying and selling the underlying coins via an exchange.
cryptocurrency working ?
Cryptocurrencies run on a distributed public ledger called blockchain, a record of all transactions updated and held by currency holders. Units of cryptocurrency are created through a process called mining, which involves using computer power to solve complicated mathematical problems that generate coins.
What is the difference between a digital currency and a cryptocurrency?
The difference between a digital currency and a cryptocurrency is that the latter is decentralised, meaning it is not issued or backed by a central authority such as a central bank or government. Instead, cryptocurrencies run across a network of computers. Digital currencies have all the characteristics of traditional currencies but exist only in the digital world. They are issued by a central authority.
cryptocurrency types ?
“Crypto can be classified into different categories, like DeFi, NFT, utility tokens, store of value tokens like bitcoin and litecoin, and yield farming tokens like Aave,” says Sidharth Sogani, CEO of Crebaco, a crypto research firm.
How do you explain crypto to a beginner?
Cryptocurrency — also known as crypto — is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange. It uses cryptography to secure and verify transactions, as well as to control the creation of new units of a particular digital currency.
5 easy steps for Here’s how to invest in Bitcoin :
- Join a Bitcoin Exchange. …
- Get a Bitcoin Wallet. …
- Connect Your Wallet to a Bank Account. …
- Place Your Bitcoin Order. …
- Manage Your Bitcoin Investments.
Is crypto real money?
Cryptocurrency is decentralized digital money that’s based on blockchain technology. You may be familiar with the most popular versions, Bitcoin and Ethereum, but there are more than 5,000 different cryptocurrencies in circulation
How To Buy Cryptocurrency ?
- Choose a Broker or Crypto Exchange. To buy cryptocurrency, first you need to pick a broker or a crypto exchange
- Create and Verify Your Account
- Deposit Cash to Invest.
- Place Your Cryptocurrency Order
- Select a Storage Method.
Frequently Asked Questions About cryptocurrency ؟
How do you earn bitcoins?
By mining, you can earn cryptocurrency without having to put down money for it. Bitcoin miners receive bitcoin as a reward for completing “blocks” of verified transactions, which are added to the blockchain.
Can I get bitcoin for free?
Yes, free Bitcoin is an absolutely legal and also legit way to earn Bitcoins. It’s a method of paying you for using or consuming specific services. Here, you need to remember that you will only receive a small portion of Bitcoin called Satoshi.
Who sets the price of bitcoin?
The price of bitcoin is determined by the market in which it trades. In other words, its price is determined by how much someone is willing to pay for that bitcoin. The market sets the price of bitcoin as same as Gold, Oil, Sugar, Grains, etc. is determined.
What is the purpose of cryptocurrency?
The main point of cryptocurrency is to fix the problems of traditional currencies by putting the power and responsibility in the currency holders’ hands. All of the cryptocurrencies adhere to the 5 properties and 3 functions of money. They each also attempt to solve one or more real-world problems.
How does cryptocurrency make money?
Some cryptocurrencies offer their owners the opportunity to earn passive income through a process called staking. Crypto staking involves using your cryptocurrencies to help verify transactions on a blockchain protocol. Though staking has its risks, it can allow you to grow your crypto holdings without buying more
Will crypto make me rich?
If you’re looking for the highest risk/reward option when trying to get rich via cryptocurrency, consider day trading. Cryptocurrency is so volatile that in the course of even a single day you can often earn significant sums
Is crypto currency safe?
Cryptos are also less regulated than many other types of investment, so there are generally fewer safeguards. When buying or selling Bitcoin, consider using an exchange with a good track record and storing your crypto in a secure hardware wallet





























